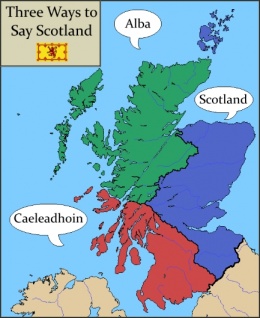
Scotland
| Conventional short name: | |
| Local: | Scotland, Álba, Caeleadhoin |
| English: | Scotland |

| |
| National motto: Ann an Dia mo dhìon dìon mi/In my defens God me defend | |
| Established: | 843 Anno Domini, {{{reason}}} |
| Languages: | |
| Official: | Scots, Gaeilg |
| Others: | Breathanach |
| Cities: | |
| Capital: | Edinburgh (Dùn Èideann), Scoun/Sgàin (ceremonial capital) |
| Other: | Glesga (Glaschu), Aiberdeen (Obar Dheathain), Dundee (Dùn Dèagh), Paisley (Pàislig), Inbhir Nis (Innerness), Dunfaurlin (Dùn Phàrlain), Stirlin (Sruighlea), Perth (Peairt) |
| Queen: | Diana I |
| Laird Chancellor o Scotland (Morair Cennsalair na h-Álba): | TBDicus Maximus |
| Area: | 77,901 km² (30,078 mi²) |
| Population: | 8,606,066 Scots/Albannaich |
| Currency: | 1 pound=20 shillings=240 pence |
| Organizations: | Federated Kingdoms, Commonwealth of Nations, League of Nations |
Much of what is known about Scotland falls under QAA rather than QSS. Known Facts about the country have accumulated gradually from various Members.
Politics
Scotland, ruled by Queen Diana I of England and Scotland, is a member of the Federated Kingdoms. Heirs to the throne of Scotland are called the Dukes of Rothesay. The country's capital city is Edinburgh, also spelled Edinbro.
Scotland is a multiparty democracy. Among others, there is a Green Carnation Party in Scotland.
Languages
Scotland is a trilingual country. The southeastern Lowlands mostly speaks Scots; Breathanach is spoken in southwest Scotland, with Gaeilg spoken in the Highlands.
Scots is a Germanic language which shares a common ancestor with English and is the language of the Lowlands and of administration in the kingdom. Scots and English saw an accelerated rate of divergence beginning in the 15th Century.
Breathanach is a Celto-Romance language. The region where it is spoken used to be the Northern Marches of Kemr. The standard form is a hybrid between the more conservative dialects of Ireland and the more innovative dialects of Scotland.
Similarly, the Gaeilg of Scotland and Ireland is considered a single language rather than two. Common Gaelic is a standard descended mostly from the speech of North Connacht and Ulster, with strong influences from Classical Gaelic and the dialects of Munster, Leinster, and Scotland. It is used in literature and on TV.
History
Charles I of England and Scotland was a believer in absolute monarchy. His attempts to wield absolute power led to a civil war in England, which resulted in the Parliament convicting the king of high treason and ordering his execution in 1649. He managed to flee to Scotland where, with Kemrese protection, he remained safe from England. After his deposal, the English Parliament proclaimed England a Commonwealth. England durign this period was governed by Thomas Rainsborough. While living in exile in Edinburgh, Charles sought allies for an invasion of England to restore the monarchy there. Kemr was hesitant to agree to an invasion of England, and dissuaded the king from an invasion. Finally, however, in 1657, after the English Parliament proclaimed Thomas Rainsborough "King Thomas I", King Donal II of Kemr at last consented to aid Charles in his effort to retake England. The so-called War of the Three Kingdoms began in late 1657, and lasted until 1661, when at last London was captured by joint Scottish-Kemrese forces. The usurper Thomas I was executed, and Charles returned to the throne of England.
Up until James IV of England and Scotland, monarchs of Scotland dubbed themselves "King/Queen of the Scots."
Slavery was abolished in both England and Scotland in 1772.
The country was overwhelmingly anti-Catholic during the reign of Mary II of England and Scotland when a political party known as the Thistles allied with the English Whigs to force the abdication of her and Constantine of England, Scotland, and Kemr.
Colonial expansion
Scotland joined with England and Kemr in colonizing parts of North America, and these colonies became provinces of the NAL. Alba Nuadh or "New Scotland" is the most conspicuously Scottish of the provinces. The province of Jacobia is also tied to the Scottish Crown. Scottish culture has played an important role in the NAL's development. General Moderator Gwrthiern ffeil Gwilim was of Scottish descent on his mother's side.
Other Scottish dominions around the world include Kingsland in Australasia, Papua New Guinea, the city of Madras, and four islands of the East Caribbean Province.
Religion
A slim plurality of Scots follow Catholicism with Reformed Protestantism as very a close second. The royal family is Catholic and the Reformation made almost no inroads into the Gaeilg-speaking Highlands and barely any into the Breathanach-speaking western coast, staying mostly a Scots-speaking, Lowlands affair. The Kirk o Scotland adheres to an episcopal polity model of administration and is Cauvinist (non-Zwinglian Reformed) in theology, following the Scots Confession of 1560, which was ratified as a compromise between Protestants in Scotland and the militantly Catholic state. Other Scots have adopted Presbyterian and Congregationalist models of church government after religious freedom statutes brought in effect by Parliament gave the common folk greater individual freedoms. The most radical reformers left the country in a rage after the Compromise of 1560 satisfied few people on either side. For this reason the majority of Scotch-descended people in the New World are descended from people who worshipped in Presbyterian or Congregationalist churches. Ironically enough, it was through the help of Scottish-American missionaries who proselytized their own homeland that restarted non-episcopal, Reformed denominations back home in Scotland. Kirk o Scotland missionaries have spread their Cauvinistic worldview and Protestant faith to other lands.
The Catholics of Scotland use the British use of the Latin Rite and are under the patriarchate of Glastonbury. Orthodox Christianity is a growing denomination amongst the Scots, although more Orthodox Christians in Scotland are still probably immigrants from the Mediterranean, Eastern Europe, and the Duine na hArd Mhacha (Na Seanchreidmhigh, "the Old Believers") from Ireland. The ratio as of the early 2020's is roughly 60/40 between naturalized immigrants and both new and generational converts, meaningly roughly 117,342 are of Greek, Slavic, Wallachian, Arab, or Duine na hArd Mhacha descent and 78,230 are of native stock.
Demographics
• Catholics: 4,370,425 (52.5%) • Kirk o Scotland (Reformed/Calvinist): 3,517,860 (42.3%) • Other Protestant (mostly Lutheran, some Baptist, sime breakaways from the Kirk o Scotland: 238,369 (2.9%) • Orthodox Christian: 195,572 (2.35%) • not religious (includes atheist, agnostic, neopagan, not practicing anything, former-Catholic, etc.): 277,976 • Muslims: 3,323 • Jews: 1,538 • Dharmic faiths: 627 • Zoroastrians: 376 Total: 8,606,066
Culture
Various sports have originated in Scotland, which include "tossing a tree" and "sweeping the ice for a rock" and "following a tiny ball to hit it with a stick", though the Irish stake claim to the final one too. In North America, colonists developed a warm-weather version of "sweeping for a rock" called whummlin.
Commonwealth Artists was founded in Scotland in 1955.
Military Insignia
Song
- ‘Will ye go to the Highlands, my bonnie love,
- Will ye go to the Highlands wi Geordie?
- An ye’ll tak the high road an I’ll tak the low,
- An I’ll be in the Highlands afore ye.
- I wad far rather stay on the bonnie banks o Spey,
- An see a the fish-boaties rowin,
- Afore I wad go to your high Highland hills,
- An hear a your white kye lowin.
- He had not been on the high Highland hills,
- Months but barely three o
- Afore he was cast into prison strong
- For huntin the deer an the roe o.
- Where will I find a bonnie little boy,
- Who will run an errand shortly,
- An who will run on to the bonnie Bog o Gight
- Wi a letter to Gighty’s lady?
- ‘Here am I, a bonnie little boy,
- Who will run an errand shortly,
- An will run on to the bonnie Bog o Gight
- Wi a letter to Gighty’s lady.’
- ‘When that ye come where the grass grows long
- Slack your shoes an run o;
- When that ye come where the bridge is broke,
- Bend your bow an swim o.
- When that ye come to Gighty’s gates,
- Stop neither to chap or call o,
- But bend your bow right clean to your breast,
- An jump right over the wall o.
- When that he came where the grass grew long
- He slacked his shoes an ran o,
- An when he came where the bridge was broke,
- He bent his bow an swam o.
- When he came to Gighty’s gates,
- He stopped neither to chap nor to call o,
- But he’s bent his bow right close to his breast,
- An jumped right over the wall o.
- When that she looked the letter upon,
- A loud, loud laugh laughed she o,
- But ere she had the half o’t read,
- The saut tear blinded her e’e o.
- ‘Go saddle to me the black horse,’ she cried,
- ‘The brown never rode so boldly,
- Until I ride to Edinburgh toon,
- To see an get life for my Geordie.’
- But when she came to yon ford mou
- The boatman he wasna ready,
- But she clasped her hands round her high horse’s neck,
- An she swam the ferry shortly.
- When that she came to the pier a Leith,
- The poor people they stood many,
- She parted the yellow gold them among,
- Bade them pray for the life a her Geordie.
- When that she came to Edinburgh toon,
- The nobles they stood many,
- An every one had his hat on his heid,
- But hat in hand stood her Geordie.
- ‘O has he killed, or has he brunt,
- O has he robbit any?
- Or what has my loved Geordie done,
- That he’s going to be hangit shortly?’
- ‘He hasna killed, nor has he brunt,
- Nor has he robbit any,
- But he’s been a-huntin the King’s own deer,
- An he’s going to be hangit shortly.’
- ‘Will the yellow gold buy off my bonnie love,
- Will the yellow gold buy off my Geordie?’ -
- ‘It’s five hundred croons if ye wad pay doon,
- Ye’ll get the hat on your Geordie.’
- She’s taen the red mantle fae her neck,
- She’s spread it oot fu bonnie,
- An she’s taen the hat oot o Geordie’s hand,
- An she’s beggit round them shortly.
- Some gave her croons and some gave her pounds,
- An some gave her hundreds many,
- An the King himsel gien her one hundred more
- To get the hat on her Geordie.
- When she was on her high horse set,
- An in behind her Geordie,
- The bird ne’er sang sae sweetly on the bush
- As she did behind her Geordie.
- Oot an spak an Irish Duke,
- An auld bow-leggit body,
- Says, ‘I wish that Gighty had lost his heid,
- Or I had gotten his lady.’
- She turned her high horse quickly aboot,
- An o but she wasna saucy,
- Says, ‘Pox be upon your Irish face,
- For ye never could compare wi my Geordie.’
- First I was lady o bonnie Auchindoun,
- An next I was lady o Gartly,
- But noo I’m guidwife o the bonnie Bog o Gight,
- An I beggit the life o my Geordie.’
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| English Members | |||
| Calcutta | East Caribbean Province (including Montserrat, a part of Ireland) | England | English Australia | English Guyana | Gibraltar | Hong Kong | Kingdom of Mauritius | Mosquito Coast | Providence Islands | The Salomon Islands | The Seychelles | Socotra | Somer Islands | Southwest Africa | Swan Islands | Wallace Cay | |||
| Scottish Members | |||
| Bombay | East Caribbean Province | Kingsland | Scotland | |||
| Cambrian Members | |||
| Ascension Island | Cambrian Arctic Ocean Territory | Cambrian Guyana | Cambrian Indian Ocean Territory | Kemr | New Kemr di'll Ostr | Madras | Mutapa | Tortuga Islands | West Caribbean Province | |||
| Other Full members | |||
| Aotearoa | Cyprus | Fiji | Grand Fenwick | Indo-British Union | Madagascar | Malta | Margarita Islands | NAL-SLC | South Africa | Tahiti | Toga | |||
| Associate Members | |||
| Alyaska | Armorica | Bharatij Samrazj | Bengal | Ireland (including Guereintia, excluding Montserrat) | Oregon | Thiruvithankur | Xrivizaja |