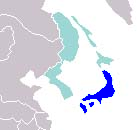
Yamato
| |
| |
| Languages | Japanese, Corean |
| Major Religions | Xintò, Buddhism, Zesucutò |
| Capital | 京都 Quiòto (temporary) |
| Government Type | Constitutional monarchy |
| King | His Majesty the Emperor |
| Regent | Maco, Princess Masaxi |
| Prime Minister | Imaidegawa Caemon |
| Area | |
| Population | |
| Establishment | Gacudai Gannen, Jùitxigaçu 4 December 7, 2004 |
| Currency | Lò = 16 Xu = 400 Fun |
| Supranational Organizations | Part of Japanese Empire |
| Major Subdivisions | 7 Regions, further subdivided into 46 Provinces |
The Kingdom of Yamato was created on Gacudai Gannen, Jùitxigaçu 4 (December 7, 2004) when the fourth amendment to the Constitution of Japan was ratified, creating a level between the Regions and the Imperial Government. Formerly, the term had been a semi-official one for the 7 regions, but there had been no actual administrative level by that name. The name is derived from an ancient term for Japan, originally the name of a particular udji (clan) in the area of modern-day Nara, whose descendants became the Emperors of Japan.
Quiòto is the temporary capital of Yamato. A new capital will be constructed on a site to be determined at a later date, after the adoption of a Constitution.
Elections for the first Yamato Parliament were held early on Gacudai 2, Sañgaçu 1 (April 6, 2005). The amendment which created Yamato requires that a constitution be approved by Gacudai 3, Jùitxigaçu 4 (December 7, 2006)
Yamato is divided into the following subdivisions, listed here with capitals (some of this may be QAA):
- Tòhocu (Sendai)
- Cantò (Edo)
- Txùbu (Nagoya)
- Quiñqui (Quiòto)
- Txùgocu (Hiroxima)
- Xicocu (Tacamaçu)
- Quiùxù (Hacata)
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| States | |||
| Yamato | Corea | Lùquiù | Ezo | |||
| Protectorate | |||
| Nittatò | |||
| Condominium | |||
| Meidji-dò |