Belarus
Belarus is a landlocked republic in Eastern Europe.
Administration
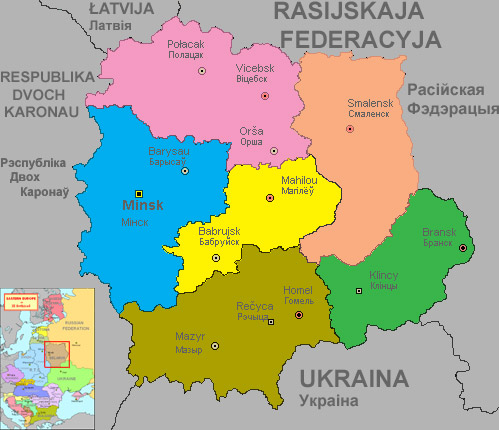
Administrative Divisions
Belarus is divided into six provinces carrying the same names as their administrative centres. In alphabetical order they are:
- Bransk
- Homel
- Mahiljow
- Minsk
- Smalensk
- Vicebsk
History
The largest part of modern Belarus used to be part of Lithuania (called 'Belaja Rus' already by the 15th century) and, being the easternmost part thereof, soon fell victim to Russia in the Partitions of the RTC. Most of eastern Belarus became Russian in the First Partition, and the rest in the Second. Belarusian culture and language are relegated to the peasants and Russian is strongly enforced.
In the course of the turmoil in Russia (triggered by GW1 and the semi-successful coup), a People's Republic of Belarus (Bielaruskaja Narodnaja Respublika) was established in Smolensk (which was not occupied by the Germans). It was quickly crushed by the Bolsheviks, who did not abolish it, however. They were in turn routed by the White Army.
After Brest-Litovsk and the establishment of Lithuania, most of modern Belarus became part of it. National tension was very strong in Lithuania, the Lithuanians suppressing the other nations, Belarusians included, and finally effectively establishing a junta in 1926. Many Belarusians looked to SNORist Russia for support, and this incited the Russians to keep the Belarusian republic in their concern for being the saviour of everyone on a pan-Slavic scale.
The end of GW2 found Russian troops well advanced into Lithuanian territory. A day before the end of the war, Russian armies entered Minsk and Maladzeczna. The western front became first the Russian occupation zone, and subsequently the Belarusian lands were incorporated into Belorussia (as the republic was now called). The enlarged Belarus became, unsurprisingly, a SNORist satellite state with pretensions on some of the RTC's territory (since many Belarusians remained in the lands to the west, which were now part of the RTC again).
After the breakup of SNORist Russia, leadership was taken by Stanislaw Szuszkewicz, leader of the Nacyjanalnaja Rada. Ever since the country has been vacillating between its strong Russian-SNORist allegiances and the dependence of its economy on the infrastructure of SNORist times and historical ties with the RTC. In April 2004, Belarus was admitted as a candidate member of the Baltic League.
The capital was moved to Minsk (or Miensk, as it is called by many) in 1992.
Geography
Borders
North: Latvia, Russia. West: Republic of the Two Crowns. South: Ukraine East: Russia.
Culture
Languages
Belarusian is the only official language but Russian is widely used in the cities. About 14.58% of the country speaks Lithuanian, of which only half actually self identities as ethnically-Lithuanian. The language is strongest in the northwest. Other languages include Ukrainian, Yiddish, and the Kypchak dialects of both the Lipka Tatars and Armenian Catholics.
Ethnic Groups
Out of 15,551,712 people:
- Belarusians 66.59%: 10,355,700
- Russians 9.3%: 1,446,310
- Lithuanians 7.29%: 1,133,720
- Jews 6.7%: 1,041,964
- Veneds 3.4%: 528,758
- Lipka Tatars 3.08%: 478,992
- Ukrainians 1.92%: 298,594
- Germans .71%: 110,604
- Armenians .41%: 63,762
- Mordvins .3%: 46,654
- Latvians .2%: 31,102
- Roma .1%: 15,552
Religion
- Christian 86.52%: 13,455,966
- Orthodox Christian (72.84% of the country, 84.19% of Christians): 11,328,632
- Exarchate of the East of the Metropolis of Kaunas (Lithuanian Orthodox): 1,774,318 (15.66% of Orthodox Christians)
- Belarusian Exarchate of the Moscow Patriarchate (Belarusian/Russian Orthodox): 9,554,314 (83.34% of Orthodox Christians)
- Catholic Church (12.78% of country, 14.76% of Christians): 1,988,136
- Latin Rite: 1,927,602
- Armenian Catholic Archeparchy of Warsaw: 51,008
- Belarusian Greek Catholic Church: 9,526
- Lutheran: 93,310 (.69% of Christians)
- Calvinist/Reformed: 33,134 (.25% of Christians)
- Oriental Orthodox: 12,754 (all Armenian Apostolic; .11% of Christians)
- Orthodox Christian (72.84% of the country, 84.19% of Christians): 11,328,632
- Jews (6.38%): 992,200
- Rabbinical/Ashkenazi: 982,244
- Lipka Tatar Karaites: 9,956
- Not religious (agnostic, atheist) 3.9%: 606,516
- Islam 2.98%: 463,478 (all Hanafi Sunnis)
- Paganism .22%: 33,552
- Lithuanian paganism: 27,994
- Tengriism: 5,558